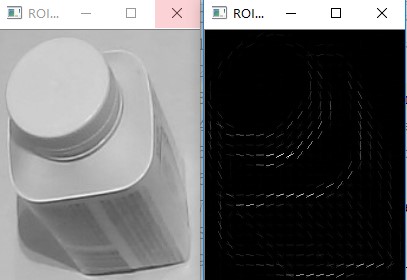
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
| #!/usr/bin/env python
#encoding:utf-8
"""
@author:
@time:2017/3/19 11:08
"""
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
from sklearn.externals import joblib
import numpy as np
import glob
import os
import cv2
from skimage.transform import pyramid_gaussian
import imutils
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage.io import imread
from extract_feature_from_fasterrcnn_labeled import get_hog
from skimage import feature
import time
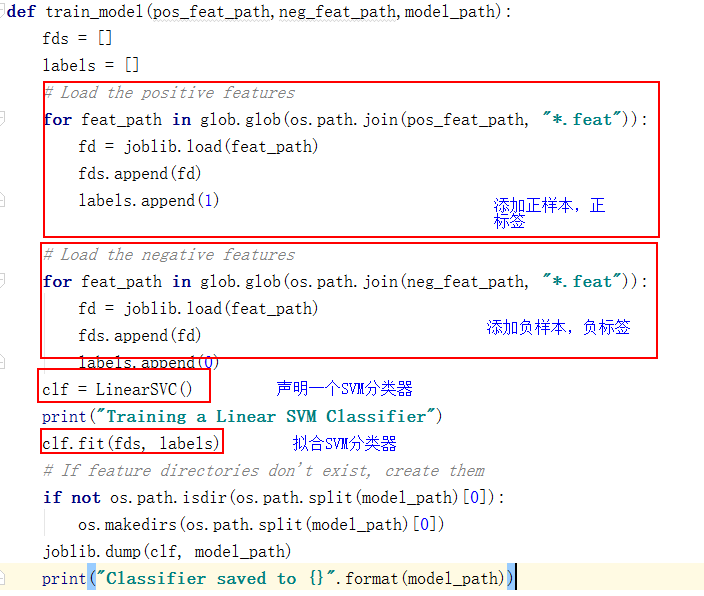
def train_model(pos_feat_path,neg_feat_path,model_path):
fds = []
labels = []
# Load the positive features
for feat_path in glob.glob(os.path.join(pos_feat_path, "*.feat")):
fd = joblib.load(feat_path)
fds.append(fd)
labels.append(1)
# Load the negative features
for feat_path in glob.glob(os.path.join(neg_feat_path, "*.feat")):
fd = joblib.load(feat_path)
fds.append(fd)
labels.append(0)
clf = LinearSVC()
print("Training a Linear SVM Classifier")
max_len = 0
for fd in fds:
if len(fd)>max_len:
max_len =len(fd)
for i in range(len(fds)):
fd = fds[i]
np.squeeze(fd[i],axis=0)
if len(fd)<max_len:
fds[i] = np.concatenate((fds[i],np.array([0]*(max_len-len(fds[i])))),axis=0)
clf.fit(fds, labels)
# If feature directories don't exist, create them
if not os.path.isdir(os.path.split(model_path)[0]):
os.makedirs(os.path.split(model_path)[0])
joblib.dump(clf, model_path)
print("Classifier saved to {}".format(model_path))
def sliding_window(image, window_size, step_size):
'''
This function returns a patch of the input image `image` of size equal
to `window_size`. The first image returned top-left co-ordinates (0, 0)
and are increment in both x and y directions by the `step_size` supplied.
So, the input parameters are -
* `image` - Input Image
* `window_size` - Size of Sliding Window
* `step_size` - Incremented Size of Window
The function returns a tuple -
(x, y, im_window)
where
* x is the top-left x co-ordinate
* y is the top-left y co-ordinate
* im_window is the sliding window image
'''
for y in range(0, image.shape[0], step_size[1]):
for x in range(0, image.shape[1], step_size[0]):
yield (x, y, image[y:y + window_size[1], x:x + window_size[0]])
def overlapping_area(detection_1, detection_2):
'''
Function to calculate overlapping area'si
`detection_1` and `detection_2` are 2 detections whose area
of overlap needs to be found out.
Each detection is list in the format ->
[x-top-left, y-top-left, confidence-of-detections, width-of-detection, height-of-detection]
The function returns a value between 0 and 1,
which represents the area of overlap.
0 is no overlap and 1 is complete overlap.
Area calculated from ->
http://math.stackexchange.com/questions/99565/simplest-way-to-calculate-the-intersect-area-of-two-rectangles
'''
# Calculate the x-y co-ordinates of the
# rectangles
x1_tl = detection_1[0]
x2_tl = detection_2[0]
x1_br = detection_1[0] + detection_1[3]
x2_br = detection_2[0] + detection_2[3]
y1_tl = detection_1[1]
y2_tl = detection_2[1]
y1_br = detection_1[1] + detection_1[4]
y2_br = detection_2[1] + detection_2[4]
# Calculate the overlapping Area
x_overlap = max(0, min(x1_br, x2_br)-max(x1_tl, x2_tl))
y_overlap = max(0, min(y1_br, y2_br)-max(y1_tl, y2_tl))
overlap_area = x_overlap * y_overlap
area_1 = detection_1[3] * detection_2[4]
area_2 = detection_2[3] * detection_2[4]
total_area = area_1 + area_2 - overlap_area
return overlap_area / float(total_area)
def nms(detections, threshold=.5):
'''
This function performs Non-Maxima Suppression.
`detections` consists of a list of detections.
Each detection is in the format ->
[x-top-left, y-top-left, confidence-of-detections, width-of-detection, height-of-detection]
If the area of overlap is greater than the `threshold`,
the area with the lower confidence score is removed.
The output is a list of detections.
'''
if len(detections) == 0:
return []
# Sort the detections based on confidence score
detections = sorted(detections, key=lambda detections: detections[2],
reverse=True)
# Unique detections will be appended to this list
new_detections=[]
# Append the first detection
new_detections.append(detections[0])
# Remove the detection from the original list
del detections[0]
# For each detection, calculate the overlapping area
# and if area of overlap is less than the threshold set
# for the detections in `new_detections`, append the
# detection to `new_detections`.
# In either case, remove the detection from `detections` list.
for index, detection in enumerate(detections):
for new_detection in new_detections:
if overlapping_area(detection, new_detection) > threshold:
del detections[index]
break
else:
new_detections.append(detection)
del detections[index]
return new_detections
def pyramid(image, scale=1.5, minSize=(30, 30)):
# yield the original image
yield image
# keep looping over the pyramid
while True:
# compute the new dimensions of the image and resize it
w = int(image.shape[1] / scale)
image = imutils.resize(image, width=w)
# if the resized image does not meet the supplied minimum
# size, then stop constructing the pyramid
if image.shape[0] < minSize[1] or image.shape[1] < minSize[0]:
break
# yield the next image in the pyramid
yield image
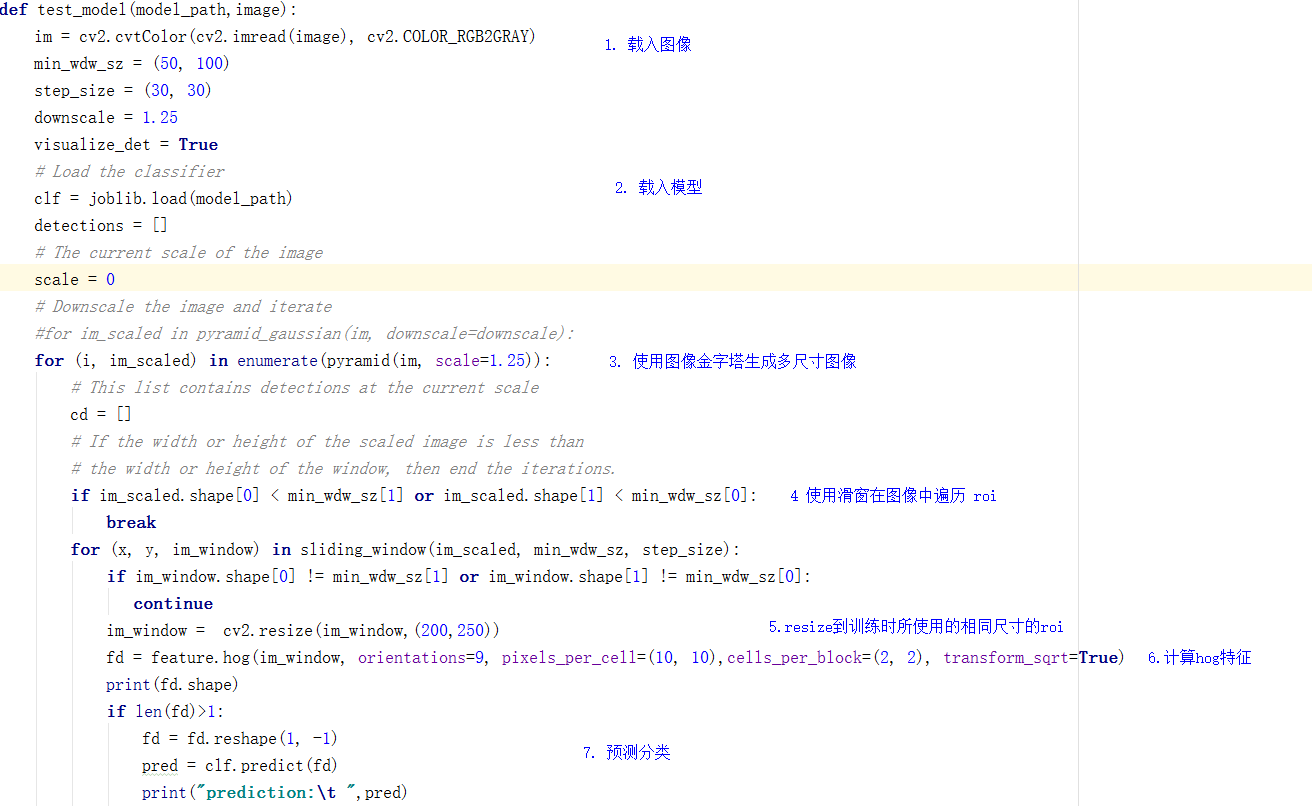
def test_model(model_path,image):
im = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread(image), cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
min_wdw_sz = (50, 100)
step_size = (30, 30)
downscale = 1.25
visualize_det = True
# Load the classifier
clf = joblib.load(model_path)
visualize_test = True
# List to store the detections
detections = []
# The current scale of the image
scale = 0
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID')
video_out = cv2.VideoWriter('D:/data/test_carmera/svm/hog_svm_slide_wid.avi', -1, 20.0, (480,600))
# Downscale the image and iterate
#for im_scaled in pyramid_gaussian(im, downscale=downscale):
for (i, im_scaled) in enumerate(pyramid(im, scale=1.25)):
# This list contains detections at the current scale
cd = []
# If the width or height of the scaled image is less than
# the width or height of the window, then end the iterations.
if im_scaled.shape[0] < min_wdw_sz[1] or im_scaled.shape[1] < min_wdw_sz[0]:
break
for (x, y, im_window) in sliding_window(im_scaled, min_wdw_sz, step_size):
if im_window.shape[0] != min_wdw_sz[1] or im_window.shape[1] != min_wdw_sz[0]:
continue
#Calculate the HOG features
#fd = get_hog(im_window)
#im_window = imutils.auto_canny(im_window)
im_window = cv2.resize(im_window,(200,250))
fd = feature.hog(im_window, orientations=9, pixels_per_cell=(10, 10),cells_per_block=(2, 2), transform_sqrt=True)
print(fd.shape)
if len(fd)>1:
#fd = np.transpose(fd)
fd = fd.reshape(1, -1)
pred = clf.predict(fd)
print("prediction:\t ",pred)
if pred == 1:# and clf.decision_function(fd)>1:
print("Detection:: Location -> ({}, {})".format(x, y))
print("Scale -> {} | Confidence Score {} \n".format(scale, clf.decision_function(fd)))
detections.append((x, y, clf.decision_function(fd),
int(min_wdw_sz[0] * (downscale ** scale)),
int(min_wdw_sz[1] * (downscale ** scale))))
cd.append(detections[-1])
# If visualize is set to true, display the working
# of the sliding window
if visualize_det:
clone = im_scaled.copy()
for x1, y1, _, _, _ in cd:
# Draw the detections at this scale
cv2.rectangle(clone, (x1, y1), (x1 + im_window.shape[1], y1 +
im_window.shape[0]), (0, 0, 0), thickness=2)
cv2.rectangle(clone, (x, y), (x + im_window.shape[1], y +
im_window.shape[0]), (255, 255, 255), thickness=2)
cv2.imshow("Sliding Window in Progress", clone)
out_img_tempt= cv2.resize(clone,(480,600))
video_out.write(out_img_tempt)
cv2.waitKey(10)
# Move the the next scale
scale += 1
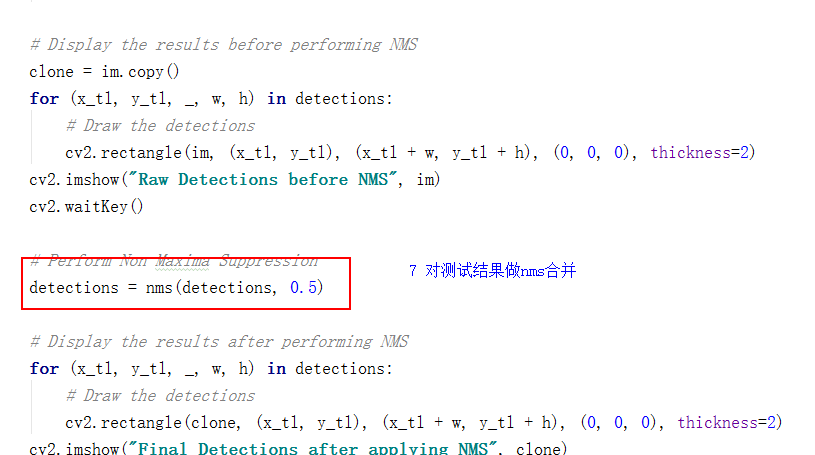
# Display the results before performing NMS
clone = im.copy()
for (x_tl, y_tl, _, w, h) in detections:
# Draw the detections
cv2.rectangle(im, (x_tl, y_tl), (x_tl + w, y_tl + h), (0, 0, 0), thickness=2)
cv2.imshow("Raw Detections before NMS", im)
cv2.waitKey()
# Perform Non Maxima Suppression
detections = nms(detections, 0.5)
# Display the results after performing NMS
for (x_tl, y_tl, _, w, h) in detections:
# Draw the detections
cv2.rectangle(clone, (x_tl, y_tl), (x_tl + w, y_tl + h), (0, 0, 0), thickness=2)
cv2.imshow("Final Detections after applying NMS", clone)
out_img_tempt = cv2.resize(clone,(480,600))
#out_img_tempt[0:clone.shape[0], 0:clone.shape[1]] = clone[:, :]
video_out.write(out_img_tempt)
cv2.waitKey()
video_out.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == "__main__":
hog_svm_model = r"D:\data\imgs\hog_svm_model_kele.model"
pos_feat_path = r"D:\data\imgs\hog_feats\2"
neg_feat_path = r"D:\data\imgs\hog_feats\2_neg"
# hog_svm_model = r"D:\data\test_carmera\svm\hog_svm_model.model"
# pos_feat_path = r"D:\data\test_carmera\svm\hog_feats\0"
# neg_feat_path = r"D:\data\test_carmera\svm\hog_feats\0_neg"
train_model(pos_feat_path,neg_feat_path,hog_svm_model)
test_img = "D:/data/test_carmera/svm/images/frmaes_2.jpg"
test_img1 = r"D:\data\imgs\images\0b24fb0ee9947292ffbb88c6e7c22a08.jpg"
test_model(hog_svm_model,test_img1)
# gray = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread(test_img), cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# edged = imutils.auto_canny(gray)
# cv2.imshow("edges",edged)
# # find contours in the edge map, keeping only the largest one which
# # is presumed to be the car logo
# (a,cnts, _) = cv2.findContours(edged.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# c = max(cnts, key=cv2.contourArea)
# # extract the logo of the car and resize it to a canonical width
# # and height
# (x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
# logo = gray[y:y + h, x:x + w]
# cv2.imshow("rect",logo)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# t0 = time.time()
# clf_type = 'LIN_SVM'
# fds = []
# labels = []
# num = 0
# total = 0
# for feat_path in glob.glob(os.path.join(train_feat_path, '*.feat')):
# data = joblib.load(feat_path)
# fds.append(data[:-1])
# labels.append(data[-1])
# if clf_type is 'LIN_SVM':
# clf = LinearSVC()
# print("Training a Linear SVM Classifier.")
# clf.fit(fds, labels)
# # If feature directories don't exist, create them
# # if not os.path.isdir(os.path.split(model_path)[0]):
# # os.makedirs(os.path.split(model_path)[0])
# # joblib.dump(clf, model_path)
# # clf = joblib.load(model_path)
# print("Classifier saved to {}".format(model_path))
# for feat_path in glob.glob(os.path.join(test_feat_path, '*.feat')):
# total += 1
# data_test = joblib.load(feat_path)
# data_test_feat = data_test[:-1].reshape((1, -1))
# result = clf.predict(data_test_feat)
# if int(result) == int(data_test[-1]):
# num += 1
# rate = float(num)/total
# t1 = time.time()
# print('The classification accuracy is %f'%rate)
# print('The cast of time is :%f'%(t1-t0))
#
|