1 概览
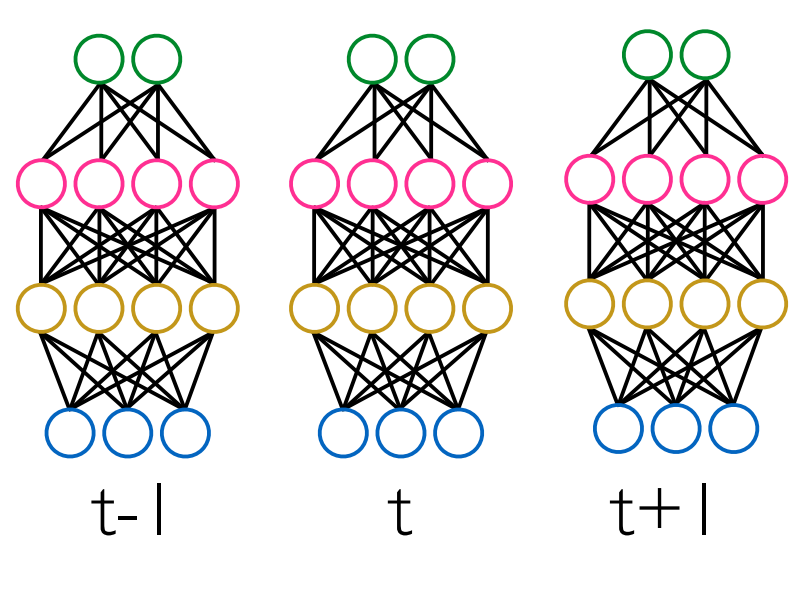
前馈神经网络
- 概念上直白的
- 对每个输入帧frame
- 执行回归得到对应的输出特征
- 为避免更广(wider)的输入上下文,可以简单的将几个frame堆叠
- 需要注意的是:语言特征已经跨越(span)了几个时间尺度(timescale)
1.1 方向
- 前馈架构
- 没有记忆
- 简单的循环神经网络
- 梯度消失现象
- LSTM神经元解决了梯度消失现象(其他类型的可能存在)
但是
- 输入和输出有相同的帧率(frame rate)
- 需要一个额外的时钟或者对齐机制来对输入做上采样
1.2 sequence-to-sequence
下一步是,集成对齐机制到网络内部
当前:输入序列长度可能与输出序列长度不一致
例如:
- 输入:上下文依赖的音素序列
- 输出:声学帧(对于声码器vocoder)
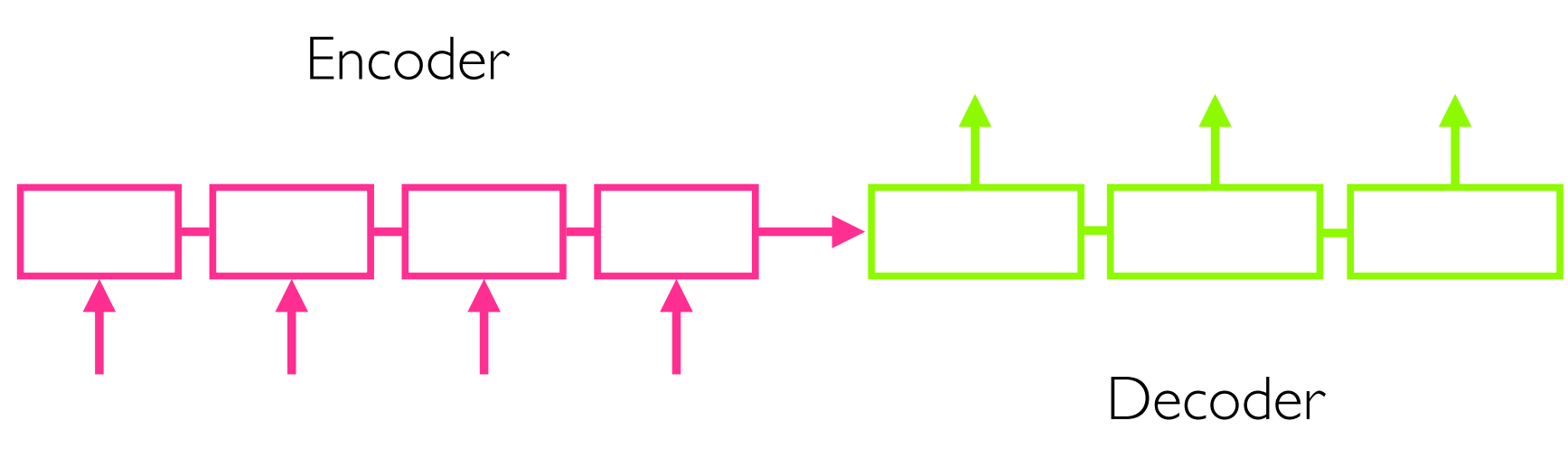
概念上
- 读取整个输入序列;使用一个固定长度的表征来记忆
- 给定表征,写输出序列
encoder(编码器)
是一个循环神经网络,读入整个输入序列,然后用固定长度表征来summarises或者memorises他们。
- encoder和decoder
1.3 sequence-to-sequence中的对齐
- 基本模型,输入和输出之间没有对齐
- 通过加入注意力模型来获得更好结果
- decoder可以接近输入序列
- decoder也可以在前一个时间步(time step)接近其输出
- 对齐像ASR模型。但是用声码器(vocoder)来做ASR效果不好
- 因而我们期望通过使用ASR样式的声学特征(仅仅是模型的对齐部分)来获得更好效果
04_prepare_conf_files.sh
1 | echo "preparing config files for acoustic, duration models..." |
05_train_duration_model.sh
1 | ./scripts/submit.sh ${MerlinDir}/src/run_merlin.py $duration_conf_file |
config files
1 | [DEFAULT] |
06_train_acoustic_model.sh
1 | ./scripts/submit.sh ${MerlinDir}/src/run_merlin.py $acoustic_conf_file |
07_run_merlin.sh
1 | inp_txt=$1 |
2 设计选择:声学模型
- 直白的方式:如果输入和输出有相同长度并且是对齐的
- 前馈神经网络
- 循环神经网络层
- 不那么直白的方式:对非对齐输入和输出序列
- 使用sequence-to-sequence
- 唯一的实践限制是,是使用什么技术,比如Theano,Tensorflow
2.1 方向
- 回归的输出是什么
- 声学特征
- 不是语音波形
所以还需要进一步
- 生成波形
- 输入时声学特征
- 输出是语音波形
3 波形生成(waveform generator)
3.1 从声学(acoustic)特征回到原始声码器(vocoder)特征
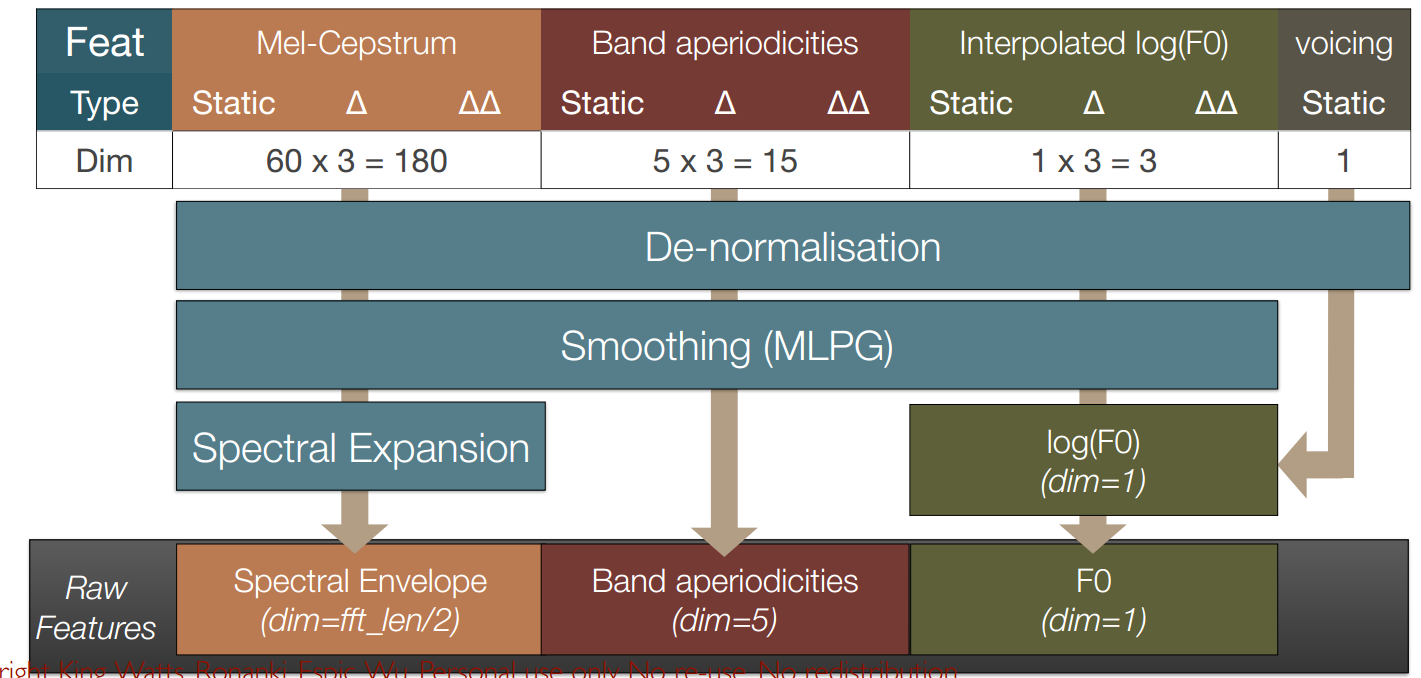
3.2 WORLD:periodic excitation using a pulse train
- 脉冲位置的计算
- 声音分割:每一个fundamental period(基本周期)创建一个脉冲,T0。从F0计算T0,其中F0之前被声学模型预测得到
- 非声音分割:固定频率 $T0=5ms$
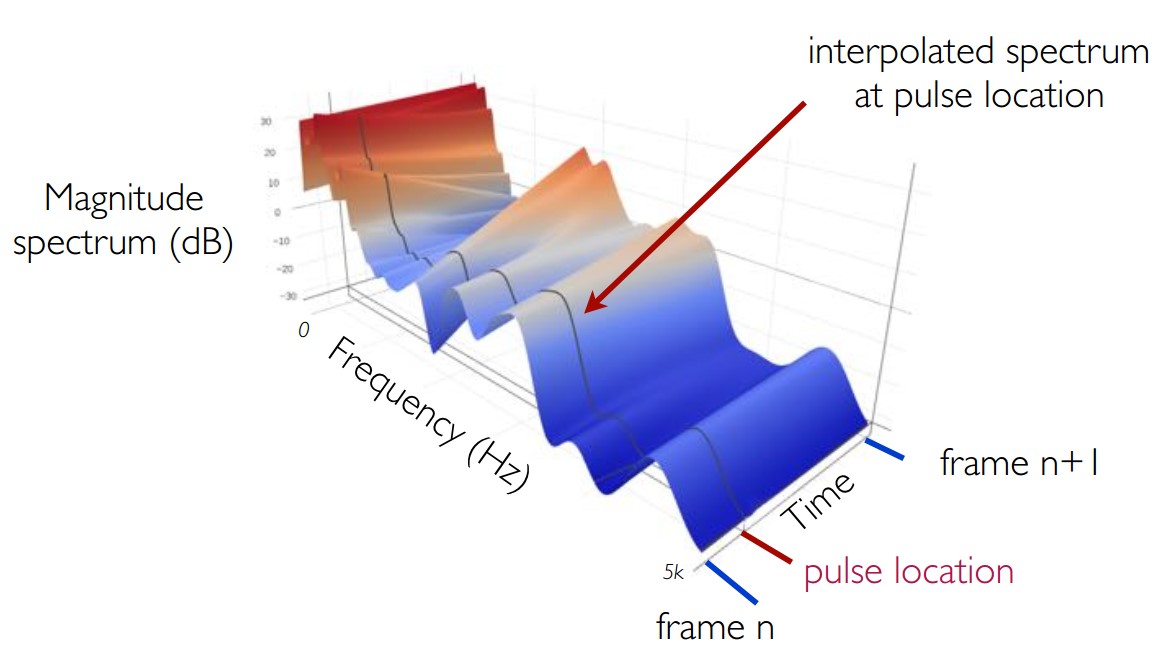
3.3 WORLD:obtain spectral envelope at exact pulse locations, by interpolation(插值法在每个确定的脉冲位置获取频谱包络)
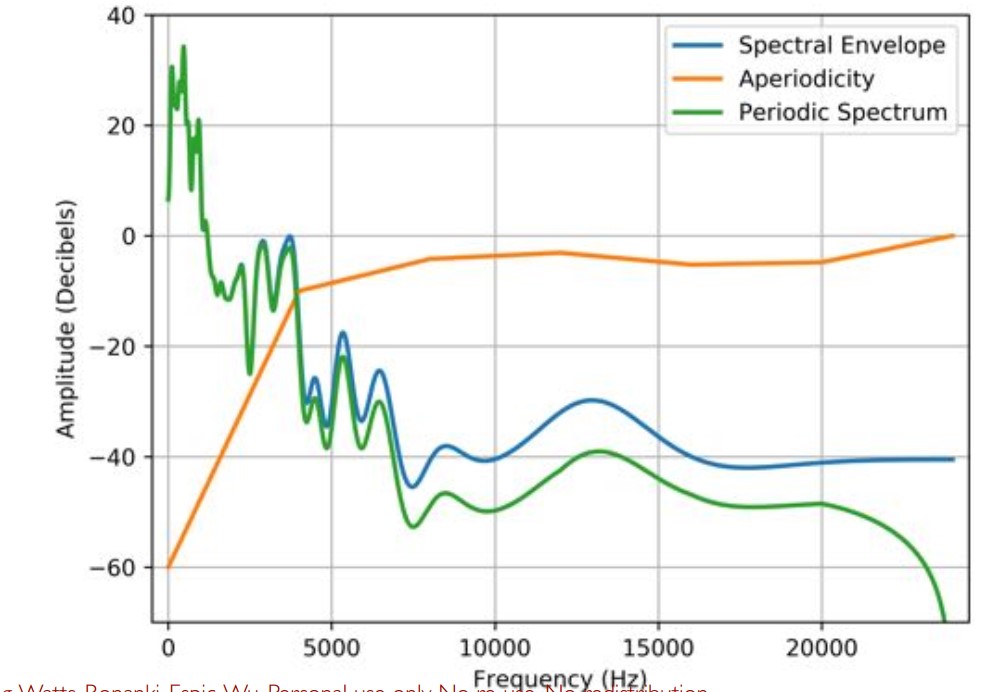
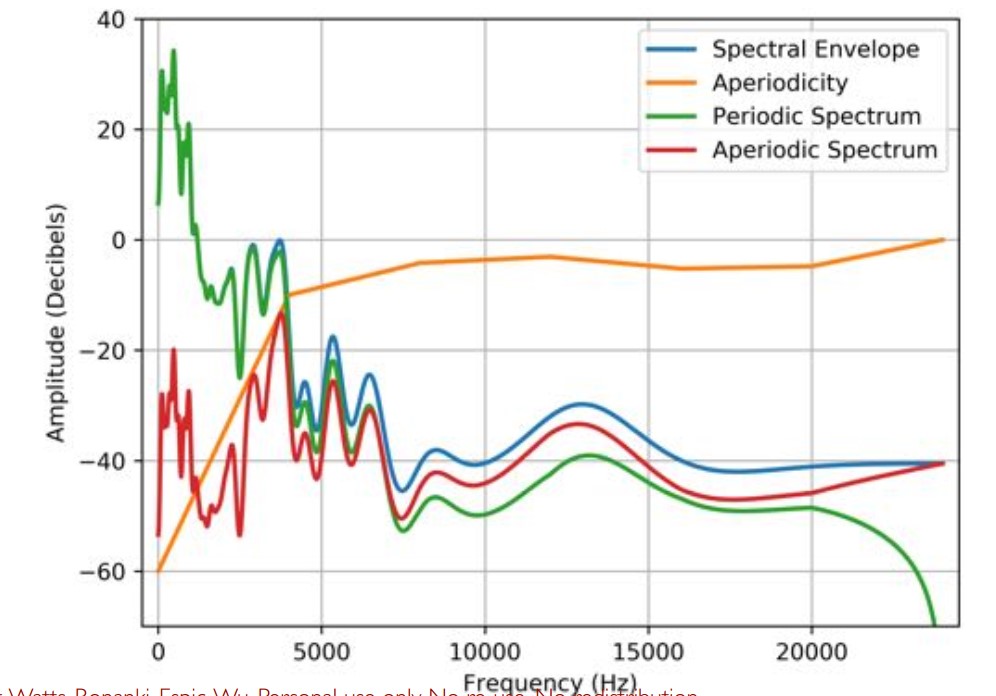
3.4 WORLD:重构周期性和非周期性的幅度频谱(magnitude spectra)
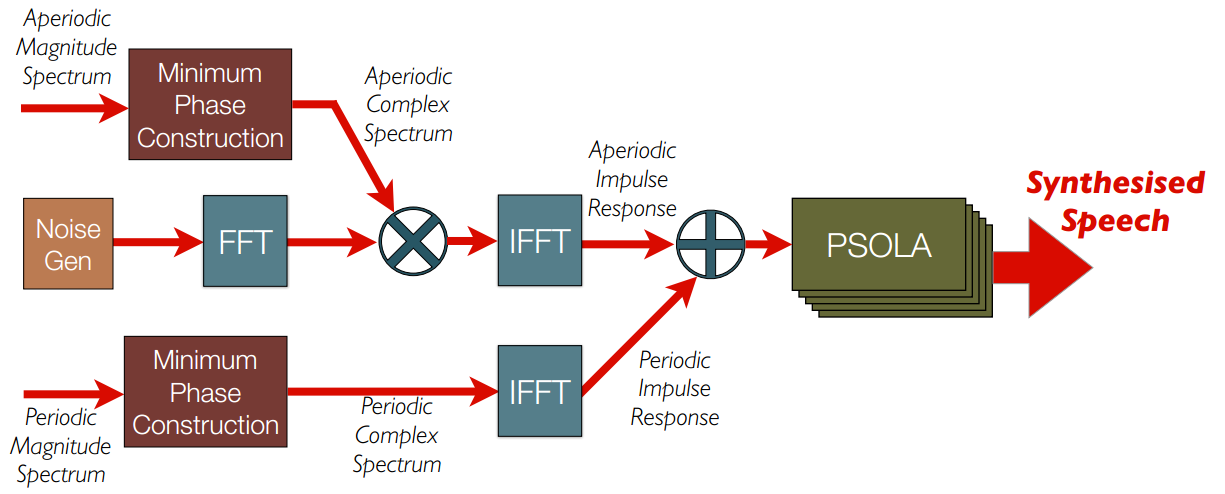
3.5 WORLD:生成波形
4 拓展
- 混合语音合成
- 使用Merlin来预测声学特征,使用Festival来做单元选取(select unit)
- 声音转换
- 输入语音而非文本
- 训练数据是对齐的输入和输出语音(而不是音素标签和语音)
- 讲话人调整
- 增强输入
- 调整隐藏层
- 转换输出
4.1 经典单元选取
此处以音素单元为例,目标和join cost
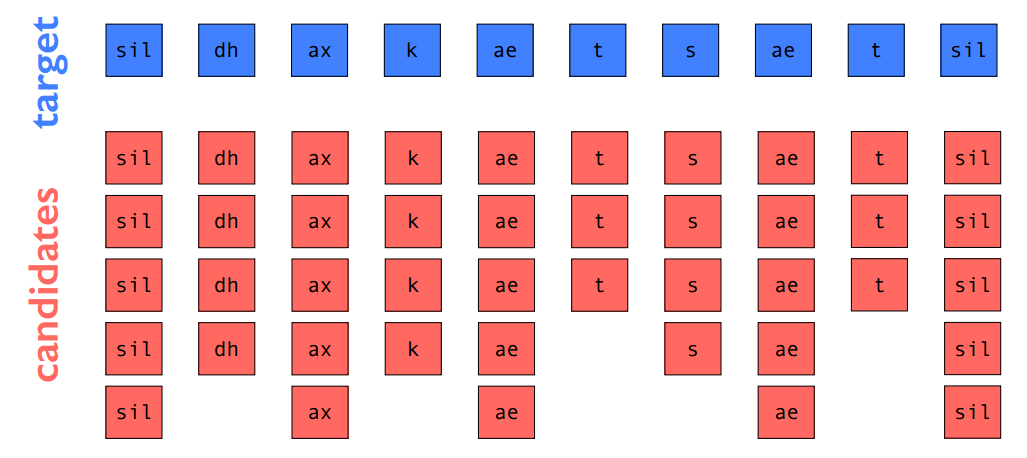
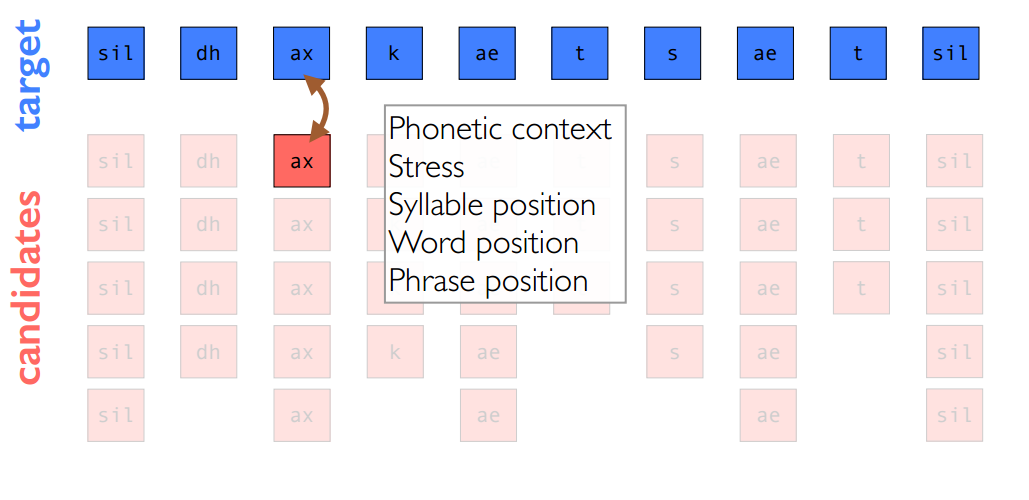
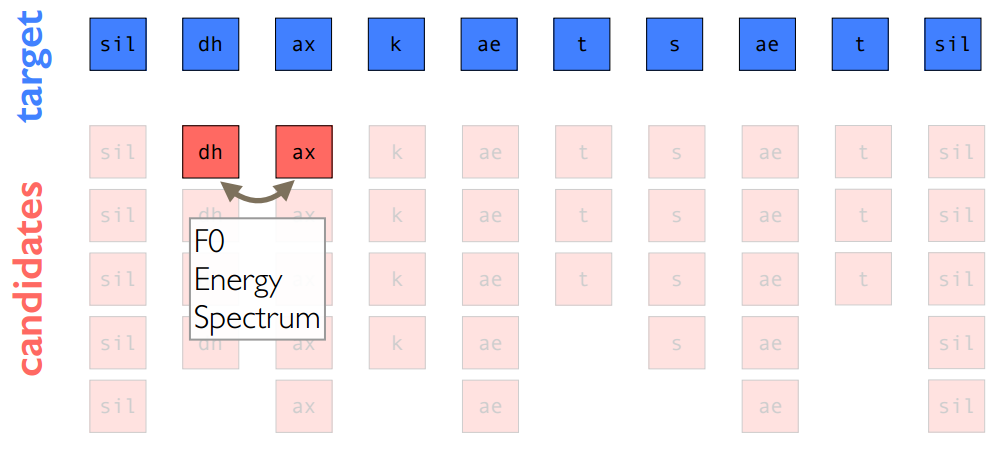
4.2 独立特征形式(Independent Feature Formulation(IFF))目标损失

4.3 声学空间形式(Acoustic Space Formulation)目标损失
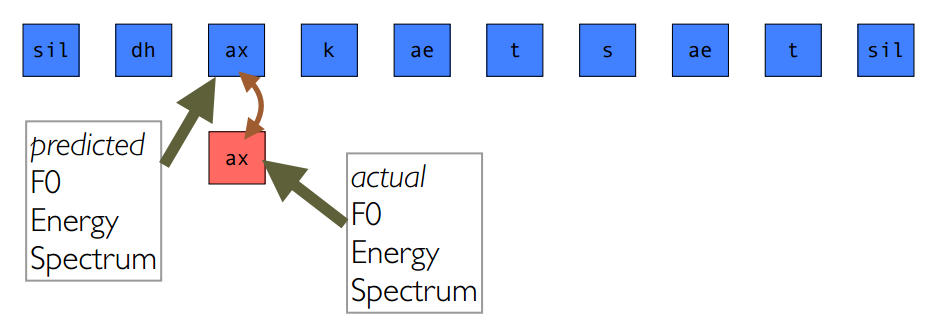
4.4 混合语音合成就像使用Acoustic Space Formulation目标损失的单元选取
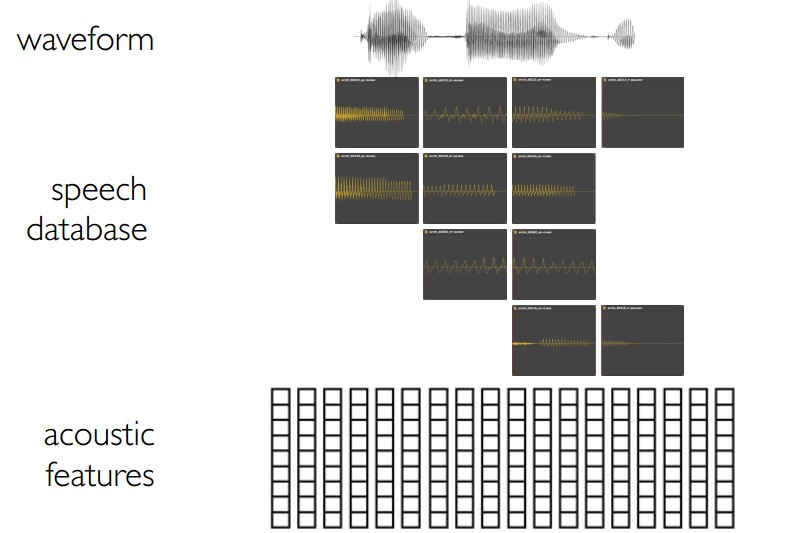
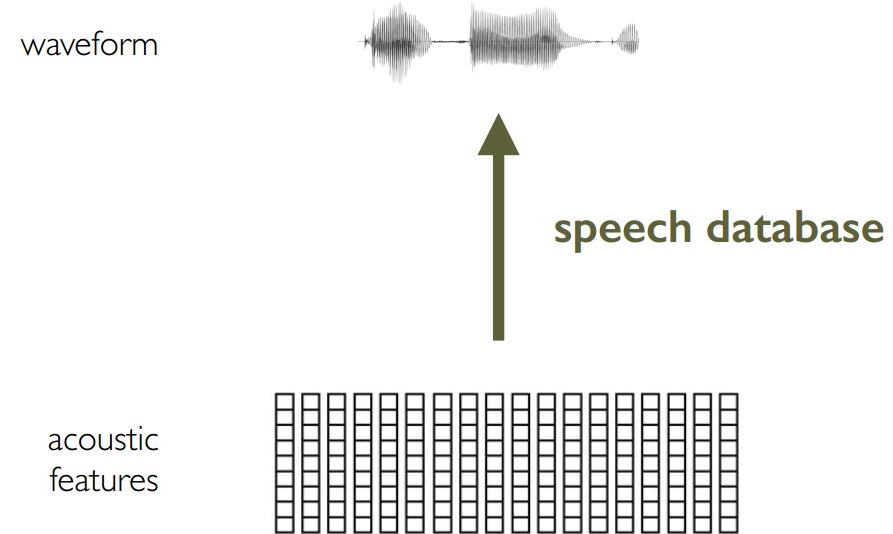
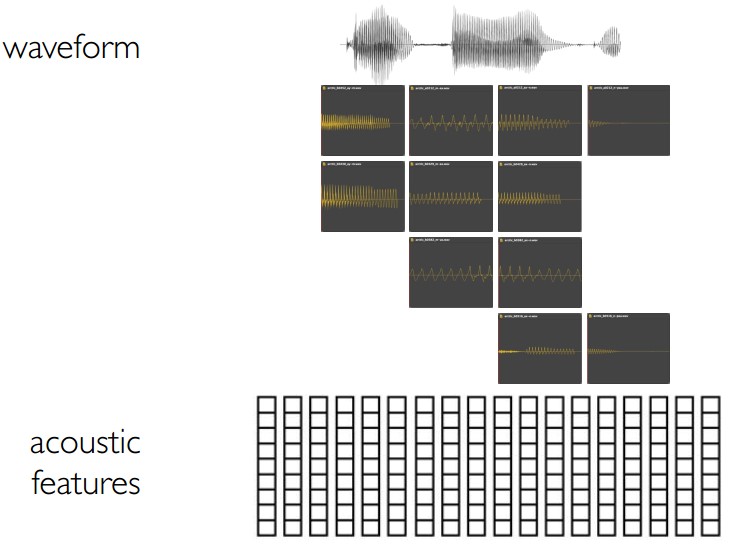
4.5 混合语音合成就像:统计参数语音合成,使用声码器(vocoder)的替换
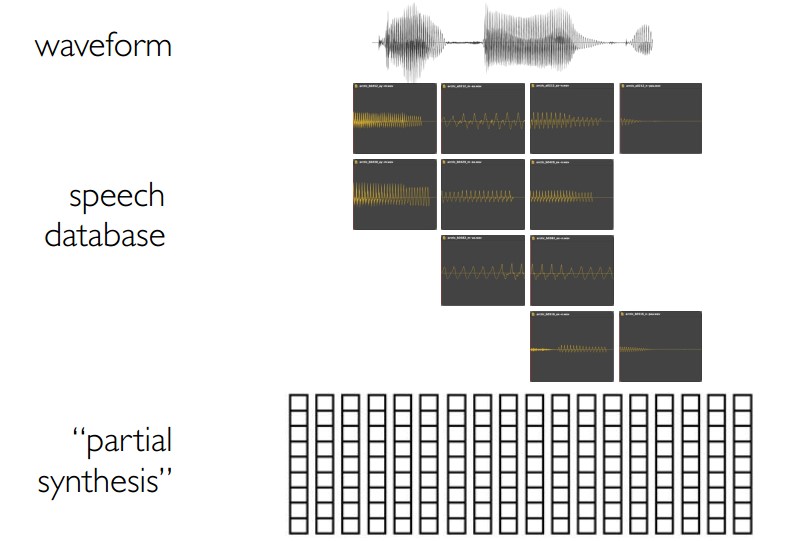
4.6 混合语音合成就像:同时对目标和join cost使用混合密度网络
7 声音转换
将源声转换为另外一个人的声音,而不改变声音内容
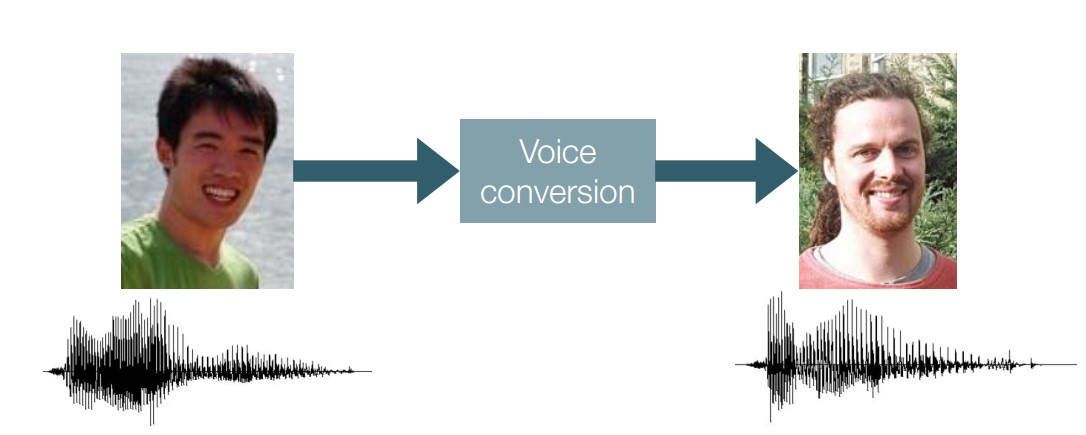
使用神经网络完成
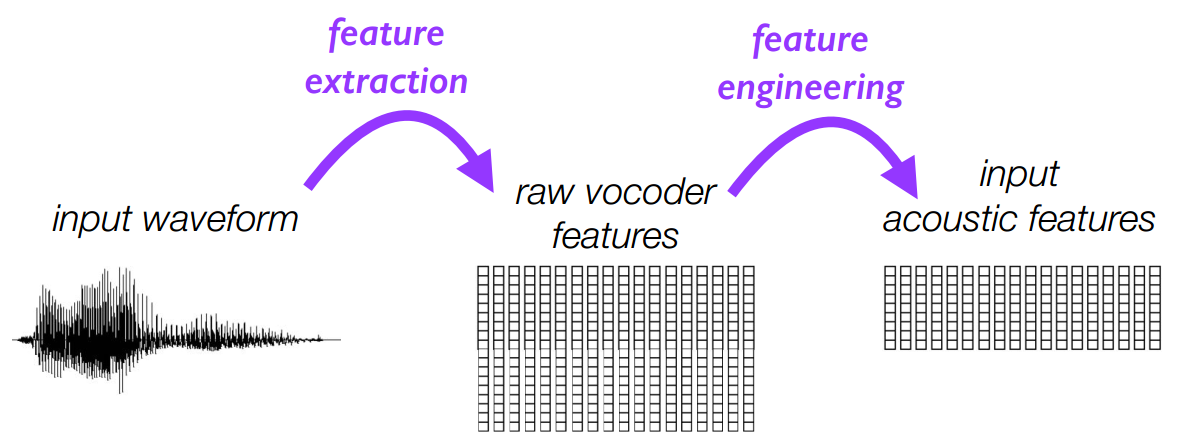
7.1 输入和输出的声学特征的抽取和工程
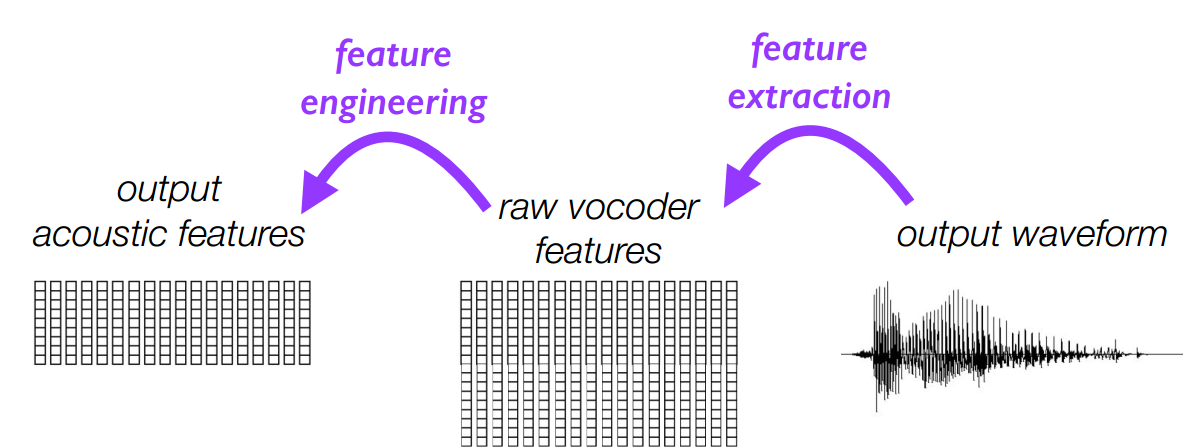
7.2 输入输出的对齐
- 从波形waveform中声学特征
- 使用动态时间封装(Dynamic Time Wraping(DTW))

7.3 最简单的方法:对齐输入和输出特征+逐帧回归
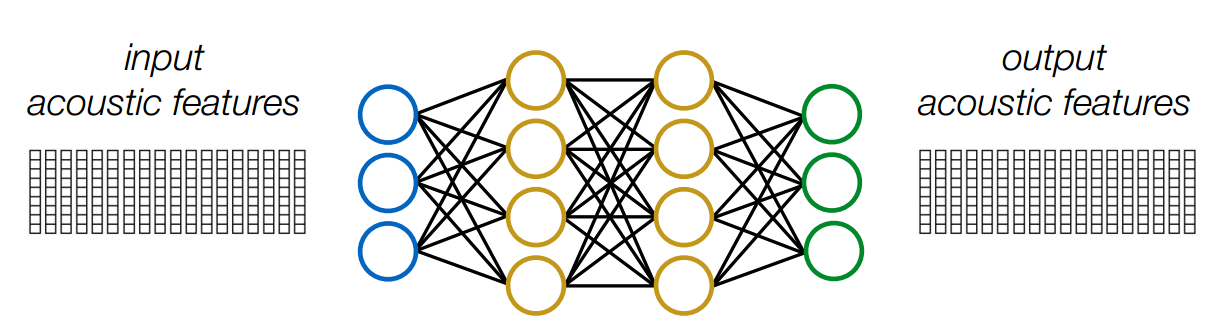
7.4 当然,我们也可以用前馈神经网络做得更好
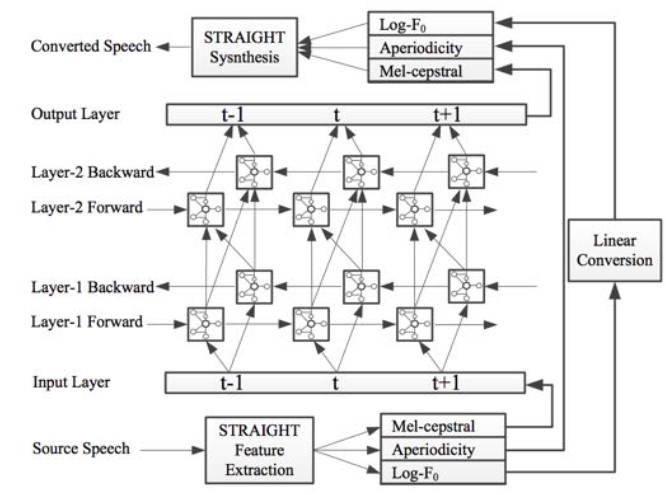
我们可以使用Merlin/egs/voice_conversion/s1/目录下的脚本完成这个工作
03_align_src_with_target.sh
1 | src_feat_dir=$1 |

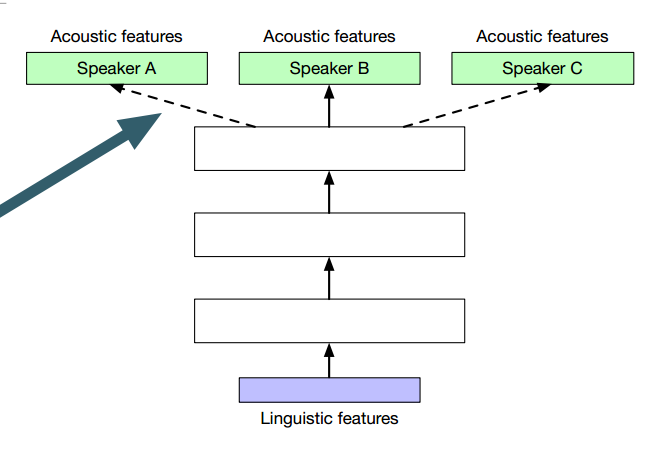
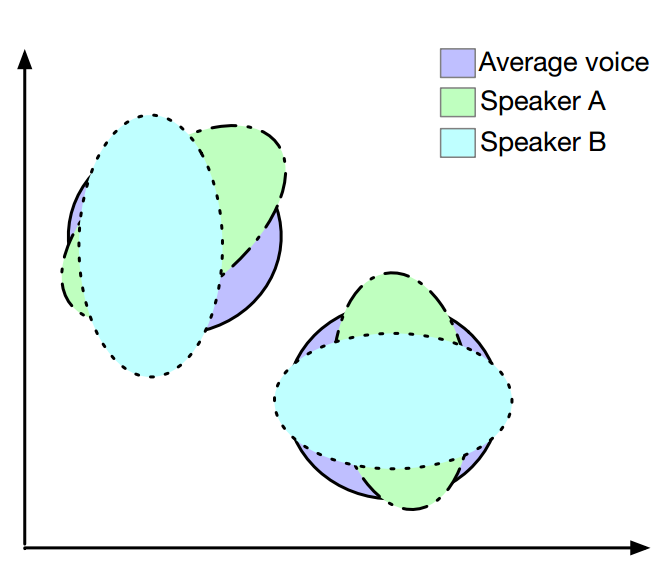
8 讲话人调整(Speaker Adaptation)
- 只使用了目标讲话人一小段录音来创造一个新的声音
8.1 使用DNN方法的讲话人调整
- 需要额外的输入特征
- 应用转换(声音转换)到输出特征
- 学习一个模型参数的修改(LHUC)
- 共享层(hat swapping)
- 在目标讲述人数据上fine-tuning整个模型
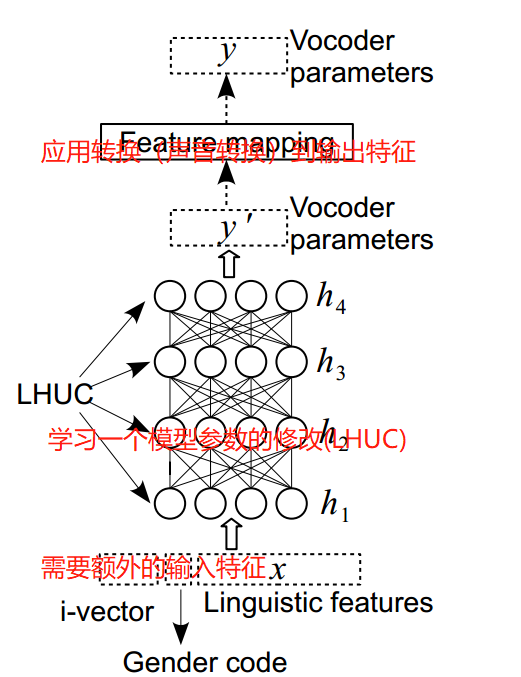
共享层和hot swapping